supraspinatus tear characteristics neer hawkins test|supraspinatus tears test : China The hug-up test, empty can (EC) test, full can (FC) test, Neer impingement sign, and Hawkins-Kennedy impingement sign were used and compared statistically for their . Resultado da See all premium you-jizz content on XVIDEOS. 1080p. Latina BBW Angelina Castro Gives Blowjob After Teasing You All Week! 6 min Angelina Castro .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Ler Dreaming Freedom Mangá Online. Choi Jungmin é severamente intimidada no ensino médio por causa de um relacionamento ruim com Ha .
Pain with this maneuver suggests subacromial impingement or rotator cuff tendonitis. One study 6 found Hawkins' test more sensitive for impingement than Neer's test.Supraspinatus muscle is the most frequently injured muscle among all other rotator cuff.7 In this section, 5 tests are presented to clinically examine supraspinatus muscle: the Neer . Our results show that the Hawkins test had a higher sensitivity in supraspinatus tendinosis and tears when correlated with MRI. Also, in diagnosing tears, the Hawkins test . The hug-up test, empty can (EC) test, full can (FC) test, Neer impingement sign, and Hawkins-Kennedy impingement sign were used and compared statistically for their .
The two most commonly used tests for impingement are Neer's Sign and the Hawkins–Kennedy test 8, 9. Neer’s sign. This test allows demonstration of a pain during passive abduction of the .
Hawkins Test technique performed by flexing shoulder to 90°, flex elbow to 90°, and forcibly internally rotate driving the greater tuberosity farther under the CA ligament.Introduction. Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings . The Neer test was developed specifically for the evaluation of the supraspinatus tendon. The Hawkins-Kennedy test was performed with the examiner facing the seated or . The Hawkins test had higher accuracy in diagnosing tears and was the most sensitive in diagnosing supraspinatus tendinosis and tears when compared to the MRI .
Therefore, a positive Neer test should be combined with an additional clinical test such as the drop-arm test to confirm the diagnosis of a supraspinatus lesion. Hawkins-Kennedy test. An . Introduction. Shoulder pain is a common complaint, with an estimated point prevalence of 6.9-26%. 1 Shoulder impingement refers to when the soft tissue structures around the shoulder joint become trapped, causing . Diagnosis can be made on physical examination with a positive Neer and Hawkins tests, and can be supplemented with MRI studies. . positive Hawkins test . positive if internal rotation and passive forward flexion to 90° .Positive Test. The Neer test is considered positive if pain is reported in the anterior – lateral aspect of the shoulder. Accuracy of Test. The Neer Test for shoulder impingement is commonly believed to be more accurate test for .
tests for meniscus tear new treatment
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing is generally performed following a full . The rotator cuff is an anatomic coalescence of the muscle bellies and tendons of the supraspinatus (SS), infraspinatus (IS), teres minor (TM), and subscapularis (SubSc) surrounding the shoulder joint (see Image. Shoulder Joint Anatomy).[1] Rotator cuff syndrome constitutes a spectrum of diseases across various pathologies associated with injuries or degenerative . - Jobe test of supraspinatus strength . - Internal lag test for rotator cuff tear - External lag test for rotator cuff tear - Neer test for shoulder impingement - Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement - Scapular repositioning test . and many studies designed to assess their test characteristics (eg, sensitivity, specificity) .
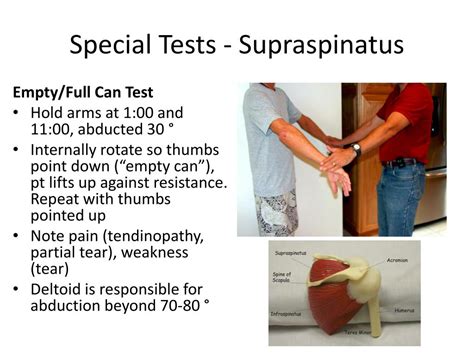
The two most commonly used tests for impingement are Neer's Sign and the Hawkins–Kennedy test 8,9. Neer’s sign. . It is indicative of a large superior cuff tear involving both supraspinatus and infraspinatus in combination. Teres minor. The examination of the posterior cuff is the hornblower sign 20. The arm is placed passively by the .Supraspinatus is the smallest of the 4 muscles which comprise the Rotator Cuff of the shoulder joint specifically in the supraspinatus fossa. . along with the Full Can Test is a commonly used orthopedic examination test for supraspinatus impingement or integrity of the supraspinatus muscle and tendon. The test is usually easier in sitting or . Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical tests, including the Jobe (empty can) test, Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test, to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis. In the Neer test, the patient was asked to sit; then, the physician put one hand on the patient’s scapula, and the other
Rotator cuff tears are common injuries caused by damage to the muscles or tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint. . Hawkins’ test. . Rotator cuff injury to supraspinatus or infraspinatus .
Neer's description was the mainstay of impingement shoulder theory for years to come. According to Neer, the supraspinatus would then undergo a predictable breakdown in three stages: edema and hemorrhage, fibrosis and tendonitis, and eventual tendon rupture. More recent thinking and research have added continued complexity to Neer's theory, and . The Neer sign and the Hawkins-Kennedy sign, commonly used to diagnose subacromial impingement, have a high sensitivity of 75–88% for supraspinatus tears.[18,19,20,21] However, these signs are characterized by a lack of specificity (<40%).[20,21] The transdeltoid palpation test, first described by Codman[] in 1934, has been used to . The Neer test was developed specifically for the evaluation of the supraspinatus tendon. The Hawkins-Kennedy test was performed with the examiner facing the seated or standing patient . The patient's arm was elevated forward at 90°, and the elbow was flexed at 90°. Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis. MRI examinations were performed on a 1.5 Tesla MRI system, and images were assessed by a blinded radiologist. .
Purpose: Clinical diagnosis of posterosuperior rotator cuff tears remains uncertain due to a lack of evidence-based consensus. This review aimed to compare the diagnostic accuracy of commonly used clinical tests for posterosuperior rotator cuff tears. Methods: The authors conducted an electronic literature search using Medline, Embase and the Cochrane . - Neer test for shoulder impingement - Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement - Painful arc sign for rotator cuff pathology - Jobe test of supraspinatus strength - Gerbers test - Posterior impingement test - Probe placement to assess subacromial impingement - Biceps tendon palpation - Biceps tendon tests The Neer test, Crank test, and Speed's test are among these tests. . The Hawkins-Kennedy test is another test for shoulder impingement. Your healthcare provider raises your arm with your elbow bent about 90 .
supraspinatus test results
supraspinatus tears test
Test Item Cluster: When this test is combined as a cluster with the Painful Arc Sign and the Infraspinatus test, and all three tests report a positive, then the positive likelihood ratio is 10.56 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is .17. If two of the three tests are positive, then the positive likelihood ratio .The Empty Can Test, along with the Full Can Test is a commonly used orthopedic examination test for supraspinatus impingement or integrity of the supraspinatus muscle and tendon. The test is also sometimes called the Empty Beer Can Test. The supraspinatus is one of the four rotator cuff muscles. Involved Structures. supraspinatus tendonIntegrity of the individual components of the rotator cuff was assessed by the strength of abduction initiation and at 90° abduction for supraspinatus tear (Jobe’s test), Speed’s and Yergason .
Also, in diagnosing tears, the Hawkins test had a higher accuracy than other tests. Therefore, the Hawkins test may be considered one of the most reliable tests for diagnosing SIS as the supraspinatus tendon is mainly affected by this syndrome. For tendinosis, the Neer test may also be considered a reliable tool due to its higher PPV.Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus.This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies.The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as: Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus .
Evidence [edit | edit source]. The infraspinatus test showed a high sensitivity of 0.90 and specificity of 0.74. Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign and the Painful Arc sign to test for subacromial impingement.If all three tests report a positive, then the positive likelihood ratio is 10.56 and if all three tests are .Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis. MRI examinations were performed on a 1.5 Tesla MRI system, and images were assessed by a blinded radiologist.
Positive Test. The Hawkins Kennedy test is considered positive if pain is reported in the superior – lateral aspect of the shoulder. Accuracy of Hawkins Kennedy Test. The Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement is commonly believed to be less accurate test for shoulder impingement than the Neer test though some studies have found the .
tests for ptfl tear
WEBSinopse. Não recomendado para menores de 16 anos. Em Coringa, Arthur Fleck (Joaquin Phoenix) trabalha como palhaço para uma agência de .
supraspinatus tear characteristics neer hawkins test|supraspinatus tears test